Leave Your Message
-
Phone
-
E-mail
Machinery belts are essential components in many industries. They facilitate the transfer of power and motion between machines. According to industry expert John Smith, “Machinery belts are the unsung heroes of mechanical operations.” They often go unnoticed, but their functionality is crucial.
These belts come in various types, including flat, V-belts, and round belts. Each type serves a unique purpose in the machinery world. For example, flat belts are commonly used for high-speed applications. In contrast, V-belts are favored for their grip and efficiency in power transmission.
However, one must consider their wear and tear. Machinery belts can degrade over time, affecting performance. Regular maintenance is often neglected, which can lead to operational failures. This oversight serves as a reminder of the importance of integrated maintenance routines in any mechanical setup. The effectiveness of machinery belts should not be taken for granted.
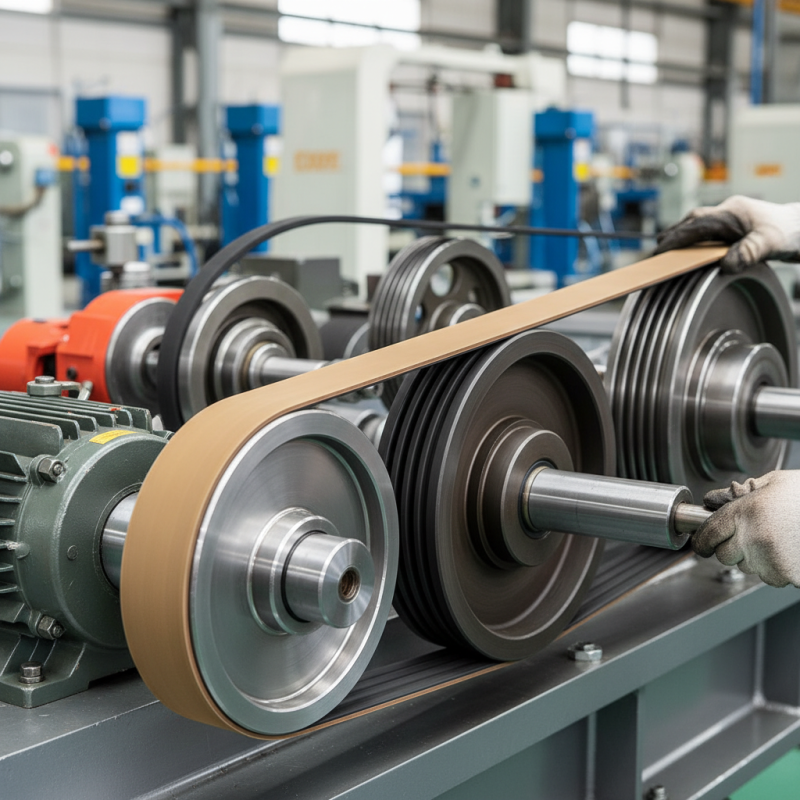

Machinery belts are essential components in many mechanical systems. They perform the critical role of transferring power between different parts of machinery. These belts are designed to connect rotating elements, like pulleys. By doing so, they enable machines to operate smoothly and efficiently.
The purpose of machinery belts goes beyond mere connection. They also help to absorb shock and vibrations caused during operation. This can prolong the life of the machinery. A well-functioning belt reduces the wear and tear on moving parts. However, belts can wear out over time and require regular checks. Neglecting this maintenance may lead to unexpected breakdowns.
Different types of belts serve various applications. Some are made of rubber, while others use materials like polyurethane or nylon. Each material offers unique advantages, but also comes with drawbacks. Finding the right balance between durability and flexibility is often challenging. Understanding these complexities is crucial for optimal performance.
| Type of Belt | Material | Typical Applications | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| V-Belt | Rubber | Automotive engines, HVAC systems | Efficient power transfer, compact size | Can slip under heavy loads, limited length |
| Flat Belt | Polyester, Cotton | Industrial machinery, conveyor systems | High load capacity, long lifespan | Wider design requires more space |
| Timing Belt | Neoprene | Automotive timing systems, printers | Accurate timing, no slippage | Potentially costly to replace |
| Chain Belt | Steel | Heavy machinery, construction equipment | Strong and durable, handles heavy loads | Heavy, may require lubrication |
Machinery belts are essential components in various industries. They facilitate the transfer of power between moving parts. Different types of belts serve specific applications based on their design and material.
V-belt is one common type. Its trapezoidal shape allows for a secure grip on pulleys. They are widely used in automotive applications and manufacturing equipment. According to industry reports, V-belts account for around 30% of the belt market due to their durability. However, they can wear down quickly under heavy loads. Regular inspection is crucial to maintain their efficiency.
Another type is the flat belt. These belts are typically used in conveyor systems. They offer low friction and can handle a wide range of speeds. Industry studies indicate that flat belts are preferred in textile and agricultural machinery. Yet, they require precise tensioning. Improper alignment can lead to slippage, diminishing performance and increasing maintenance costs. Understanding these nuances helps optimize the use of machinery belts effectively.
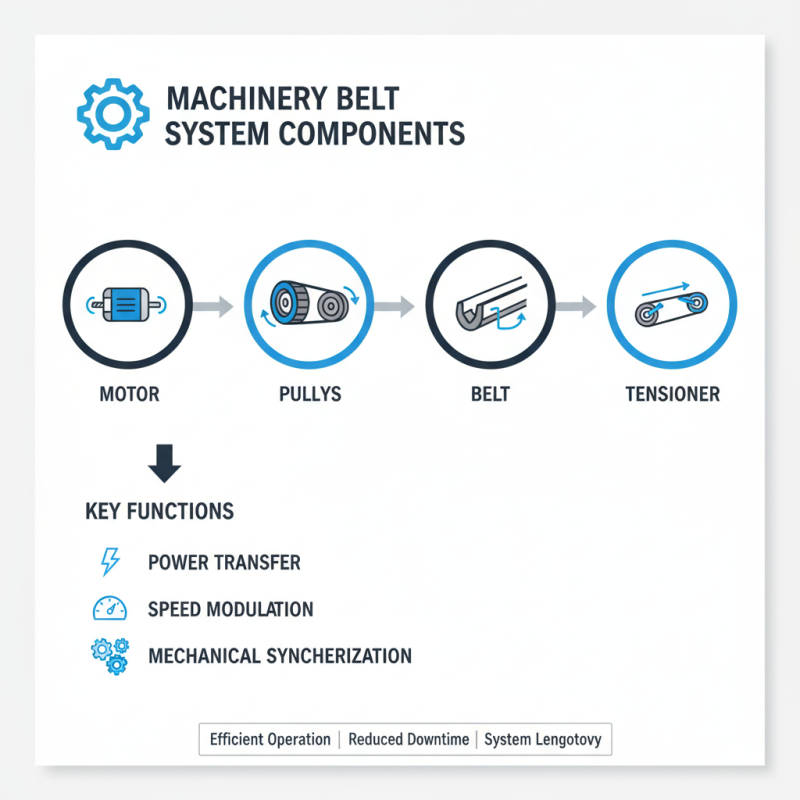
Machinery belts are essential components in various mechanical systems. They facilitate the transfer of power between pulleys. Understanding the components of a machinery belt system is crucial for efficient operation. These systems typically include belts, pulleys, tensioners, and motors. Each part plays a distinct role in the overall functionality.
The belt is the heart of the system. It is often made of rubber or synthetic materials. These materials provide the necessary grip to prevent slipping. Pulleys guide the belt and help in changing the direction of motion. Tensioners are vital for maintaining proper belt tension. A loose belt can lead to inefficiencies and potential breakdowns.
In practice, installation can be tricky. Misalignment of pulleys often occurs, affecting performance. Regular maintenance is necessary to ensure all components function correctly. The life span of a belt can vary significantly. Environmental factors like temperature and humidity influence durability. Some users may overlook these details, leading to unexpected failures. Therefore, it's essential to pay attention to both the components and how they interact.
Machinery belts are essential components in many machines, serving a variety of functions. These belts transfer power between pulleys. They can accelerate, decelerate, or change the rotational direction of a machine's components. For instance, in a conveyor system, belts move materials efficiently through different production stages. The right tension ensures optimal performance.
The mechanics of these belts involve friction and material properties. The surface of the belt must grip the pulley effectively. If the grip is too loose, slippage occurs. Conversely, if too tight, it can cause wear. Various materials like rubber or polyurethane are commonly used. They provide flexibility and durability, but they also have limitations. For example, excessive heat can lead to melting or degradation.
Understanding these mechanics can be challenging. Each belt must be tailored to the machine's operation. Misalignment can lead to premature failure. It's crucial to regularly inspect and maintain belts for maximum efficiency. The balance between tension and flexibility is delicate. Ignoring these details can result in larger operational issues down the line.
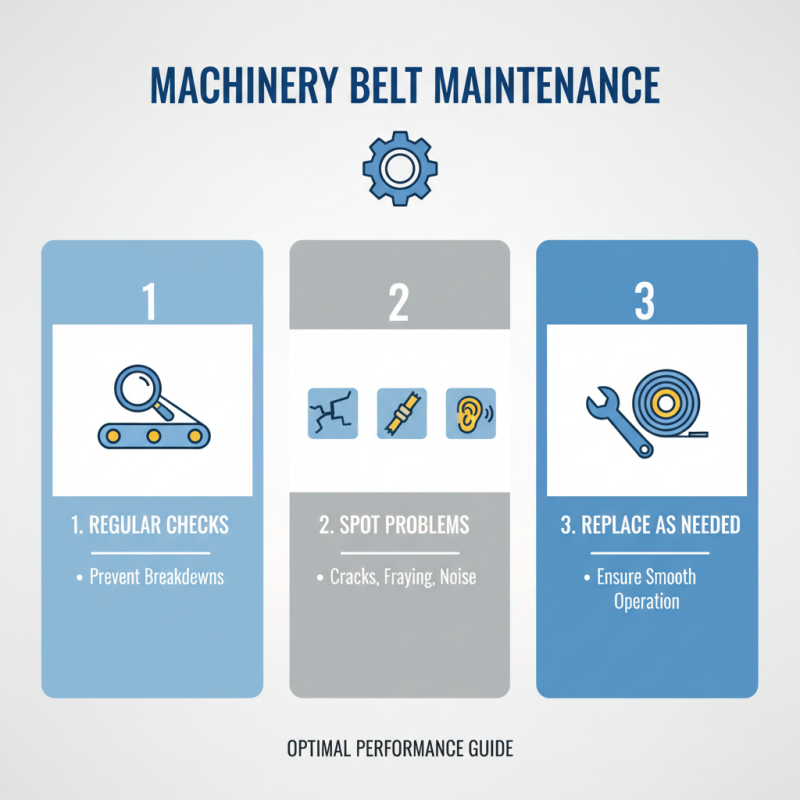
Maintaining machinery belts is crucial for optimal performance. Regular checks can prevent unexpected breakdowns. Look for signs of wear and tear. Cracks, fraying, or unusual noise indicate issues. Replace belts as necessary to ensure smooth operation.
Troubleshooting can seem daunting. Begin by inspecting alignment. Misalignment causes premature wear. Adjust the pulleys if needed. Tension is another critical factor. Too loose or too tight can lead to problems. A simple tensioning tool may help.
If belts slip during operation, it may signal further issues. Check for oil or dirt on the belt. These contaminants can reduce grip. Cleaning or replacing belts can make a difference. Regular attention to these areas can prolong the life of machinery belts, saving time and money in the long run.